
The reasoning for this is because AFI increases the detection of oligohydramnios, resulting in increased rates of induction without improving outcomes for babies. 2017 Nebhan & Abdelmoula 2008 Magann et al. Studies comparing the two methods conclude that the ‘maximum pool’ measurement is the ‘better choice’ ( Coombe-Patterson et al.

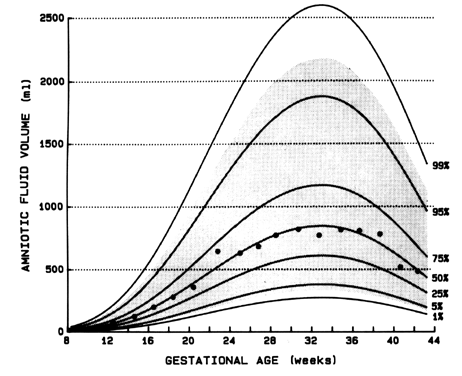
Maximum Vertical Pool (MVP): The ‘single deepest vertical pocket’ of fluid is identified and measured.īoth tests measure amniotic fluid in cms amniotic fluid with ‘normal’ values considered to be 5cm to 25cm.Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI): four ‘pockets’ of fluid are measured by ultrasound and added up.There are two types of ultrasound tests aimed at assessing AFV: Here is the first problem… there is no accurate method for measuring AFV. However, measurement and thresholds of normal/abnormal are not clear. Too much fluid is called ‘polyhydramnios’ and too little fluid is called ‘oligohydramnios’. The amniotic sac and fluid play an important role during pregnancy and birth and you can read more about that in this post.Ībnormalities in AFV occur when there is an imbalance between fluid production and clearance. Amniotic fluid volume reduces from 37 weeks gestation. Therefore, lower volumes of urine are excreted into the amniotic sac. As the baby’s kidneys mature, urine becomes more concentrated. 2012). From day to day there is little change in AFV, however volume decreases towards term. Maternal hydration is also associated with AFV ( Patrielli et al. The balancing act required to maintain a healthy AFV may be influenced by hormones (prolactin and prostaglandins), osmotic and hydrostatic forces, and the baby. direct flow across the amnion (placental membrane) into placental blood vessels.the baby swallowing fluid and passing it back into mother’s blood stream.Amniotic Fluid Volume Regulation Regulation of amniotic fluid in the second half of pregnancyĪmniotic fluid is in a constant state of circulation. In the second half of pregnancy, the primary sources of fluid production are from the baby:Īnd the main sources of fluid clearance are: In fact, this post probably raises more questions than answers! Also note that I am focussing on AFV at term. I use the word ‘may’ quite a bit in this post because little is known about AFV, therefore a lot of the available information is theoretical. Most of the content is available in textbooks and I have provided references/links for research where I have stepped outside textbook sources. One study revealed that drinking more fluids is also good for increasing amniotic fluid levels in women between 37 and 41 weeks of pregnancy.This post is in response to readers asking me to cover the topic of induction for low amniotic fluid volume (AFV). Here are some ways to improve your amniotic fluid levels.ĭoctors recommend pregnant women to drink plenty of water. If you're less than 36 weeks pregnant, you need to go through extra monitoring to make sure your baby is in good shape. Treatment methods will depend on the cause and how far your pregnancy is.

It should be treated promptly by your doctor. Having low amniotic fluid can put you or your baby at risk if not treated properly. This condition can occur at any time during pregnancy, but it is most common during the last trimester.
Low amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios) is a condition in which the amniotic fluid measures lower than expected for a baby's gestational age. The health and well-being of your baby is determined by the amount of fluid present in the amniotic sac. It also facilitates the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and foetus.

The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid that serves as a cushion for the growing foetus. Written by Longjam Dineshwori |Published : Ma6:11 PM IST


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
